Sorghum
Sorghum is one of the most important cereal crops of the hotter and drier regions ofthe tropic and sub tropics, preferred crop in uncertain and erratic rainfall areas.
It is a superior grain for brewing because of its good malting capacity.
Sorghum has few disease and insect pest problems in Zambia. Birds are the main concern. Traditional varieties of sorghum require a long growing season, have low yield potential, and are tall and non-responsive to improved management. Improved sorghums, however, are high yielding, input responsive, and far more resistant to drought.
| Variety | Characteristics | |
| 1. | Kuyuma | Type: Open-pollinated variety, medium maturing |
| Tolerance: Excellent to drought and anthracnose. | ||
| Days to maturity: 100-110 | ||
| Grain colour: White | ||
| Seed rate: 12kg/ha | ||
| Spacing: 90 x 25cm | ||
| Target regions: I, II | ||
| Yield potential: 4,000-6,000kg/ha | ||
| 2. | ZMS-36R | Type: Open-pollinated variety, medium maturing |
| Tolerance: Excellent to drought and anthracnose. | ||
| Days to maturity: 100-110 | ||
| Grain colour: White | ||
| Seed rate: 12kg/ha | ||
| Spacing: 90 x 25cm | ||
| Target regions: I, II | ||
| Yield potential: 4,000-6,000kg/ha |
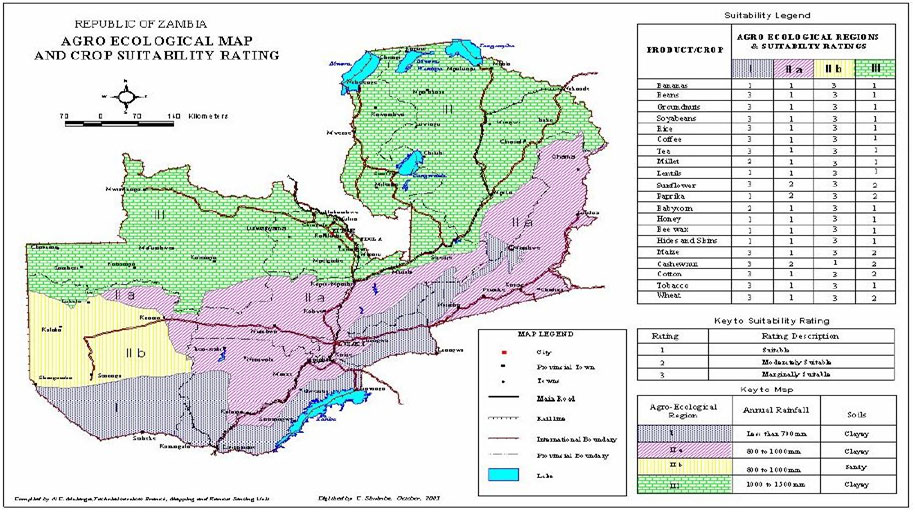
1-ZAMBIA’S AGRO-ECOLOGICAL ZONES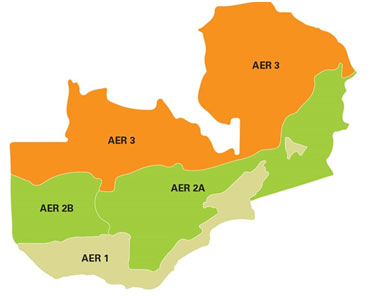
Key
AER 1 = Agro-Ecological Region 1
- Less than 800mm rainfall per year.
- 80-120 effective growing days.
- Suitable for millet, sorghum, maize, groundnuts, soyabeans.
AER 2A and AER 2B = Agro-Ecological Region 2a and Agro-ecological Region 2B
- 800-1, 000mm rainfall per year.
- 100-140 effective growing days.
- Suitable for maize, sorghum, millet, cowpea, groundnuts, soyabeans.
AER 3 = Agro-Ecological Region 3
- More than 1, 000mm rainfall per year.
- 160+ effective growing days.
- Suitable for maize, millet, sorghum, groundnuts, beans, rice, soyabean
C.2-ZAMBIA’S AGRO-ECOLOGICAL ZONES